Harshith Manufacturers Pvt. Ltd. is a Pre-engineered building (PEBs) manufacturer in Uttarakhand & India,
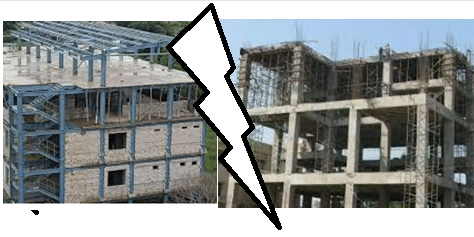
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) and conventional buildings are two distinct construction methods with their own advantages and considerations. Here’s a comparison between the two:
Comparison Between Pre Engineered Buildings and Conventional Buildings
Design and Construction Time: PEBs: Pre-engineered buildings are designed and manufactured off-site in a factory-controlled environment. They are based on standardized components and can be quickly assembled on-site. This significantly reduces construction time compared to conventional buildings.
Conventional Buildings: Conventional buildings require more time for design and construction. Each component is typically custom-designed and fabricated on-site, which can lead to longer construction schedules.
Cost: PEBs: Due to their standardized design and streamlined manufacturing process, PEBs are generally more cost-effective than conventional buildings. The use of pre-engineered components and faster construction time can result in lower labor and material costs.
Conventional Buildings: Conventional buildings often involve more complex design and construction processes, which can lead to higher costs. Customization, extensive labor, and longer construction schedules may contribute to increased expenses.
Flexibility and Customization: PEBs: Pre-engineered buildings offer a certain level of flexibility in terms of layout and design. However, their design is based on pre-engineered components, limiting customization options. Changes or modifications to the building’s layout or design may be challenging.
Conventional Buildings: Conventional buildings allow for greater flexibility and customization. Architects and engineers can design structures according to specific requirements, incorporating unique features and architectural elements.
Structural Strength and Durability: PEBs: Pre-engineered buildings are designed to meet specific structural requirements, considering factors such as wind loads, seismic activity, and snow loads. The steel components used in PEBs offer strength and durability, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Conventional Buildings: Conventional buildings can also be designed to meet required structural standards. However, the strength and durability depend on the quality of materials used and the construction techniques employed.
Application and Size: PEBs: Pre-engineered buildings are well-suited for a range of applications, including warehouses, industrial buildings, sports facilities, and commercial structures. They are particularly advantageous for large-span structures.
Conventional Buildings: Conventional buildings can be designed for various applications, from residential houses to high-rise buildings. They offer greater flexibility in terms of architectural design and aesthetics.
Maintenance and Longevity: PEBs: PEBs are typically low-maintenance structures. The steel components used in PEBs are resistant to corrosion, pests, and fire. Regular inspections and maintenance can ensure their longevity.
Conventional Buildings: Maintenance requirements for conventional buildings depend on the materials used and the quality of construction. Additional maintenance may be needed for specific materials such as wood or concrete.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between pre-engineered buildings and conventional buildings depends on factors such as budget, project timeline, required customization, and specific project needs. Both methods have their advantages and are suitable for different applications. It’s essential to evaluate these factors and consult with professionals to determine which approach is best for your specific project.